Transformer Knowledge
1.Definition of transformer
A transformer is a static electrical device that uses the principle of electromagnetic induction to convert the input AC voltage into the required output voltage of the same frequency to meet the needs of high-voltage power transmission, low-voltage power supply and other purposes.

2. The role of transformer
(1) Transmitting electric energy is convenient and economical. In the process of transmitting electric energy, the voltage is always increased, because when transmitting a certain amount of electric power, the higher the voltage, the smaller the current. This can save wires and other costs, and can reduce the loss on the wires during power transmission.
(2) The output voltage of the generator is low, far less than the needs of high-voltage transmission lines. This requires a transformer to boost the voltage, and after the electric energy is sent to the power consumption area, it needs to be stepped down through a step-down transformer.
3. Working principle of transformer
The main components of the transformer are the core and the two windings wrapped around the core. The two windings are only magnetically coupled but not electrically connected. Adding alternating voltage to the primary winding generates alternating magnetic flux linking the primary and secondary windings, and induces electromotive force in the two windings respectively.
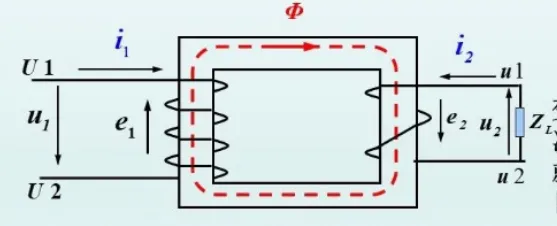
As long as (1) the magnetic flux changes; (2) the number of turns of the primary and secondary windings is different, the purpose of changing the voltage can be achieved.
4. Classification of transformers
(1) Divided by use: power transformers and special transformers.
Power transformers are further divided into step-up transformers, step-down transformers and distribution transformers.
(2) According to the number of windings: single winding (auto-coupling) transformer, double winding transformer, three winding transformer and multi-winding transformer.
(3) According to the number of phases: single-phase transformer, three-phase transformer.
(4) According to the core structure: core transformer and shell transformer.
(5) According to the voltage regulation method: non-excitation voltage regulating transformer and on-load voltage regulating transformer.
(6) According to cooling medium and cooling method: dry-type transformer, oil-immersed transformer and gas-filled transformer.
(7) According to the neutral point insulation level: full insulation and graded (semi) insulation.

